· 5 min read
Hey Neo, how many languages do you speak? – Multilingual domains for chat and voice bots
Use cases for the Multi2ConvAI research project - Corona chatbot, voice assistant for quality assurance and assistant for Last-Mile-Delivery
Voice assistants and chatbots offer a decisive advantage in use: they are very easy for users to use because they adapt to the user and understand “his” language - at least that’s the goal. In reality, however, it is often necessary to remember specific commands and formulate requests in such a way that they are understood by the chatbot. But why is that? Shouldn’t an “artificial intelligence” be able to understand natural language?
The problem here is not primarily based on the technology, but also in the creation and maintenance of the training data for natural language understanding. This is often done via a tool in the background. The language model is trained via a manual classification of previous dialogs and the curation of responses: Content must be maintained and data models have to be successively improved based on real interaction data. This process can be time-consuming for one language alone – what about when we want to support 5, 20, or 100 languages?
The goal of the research project
The Multi2ConvAI research project addresses exactly this problem: In real-world use cases, it often happens that models have to be trained on small specific corpora or - in extreme cases - without available dialogs in a target language or domain. The research project thus evaluates methods for transferring conversational AI models to different domains and languages.
Choice of use cases
It is particularly important for the research project to establish a practical reference and not to start from wishful thinking: In reality, there is often little or even no training data available in the first step; this usually has to be built up iteratively with users. Therefore, the research project focuses on use cases in which training data is only available to a limited extent. Furthermore, it is important for the research project to map different complexities in dialogs and data, based on different use cases and to identify use cases in which multilinguality plays a decisive role: For example, a FAQ chatbot behaves differently than a voice assistant in a quality process at different locations.
Corona chatbot: Important questions answered quickly
Classic chatbots are primarily used for high volume and easy accessibility. The Corona pandemic has created massive challenges for many institutions and facilities: How to accurately handle a high volume of requests in a short time?
Neohelden worked with several customers during this time to develop chatbots in just a few days that took on precisely this task. On the one hand, this ensures high availability and scalability in the processing of requests, and on the other hand, it allows the assistant’s “human colleagues” to focus on complex and individual cases. In addition to the automation potential, chatbots also increase accessibility: they are available on the smartphone and web via chat or even via voice control.
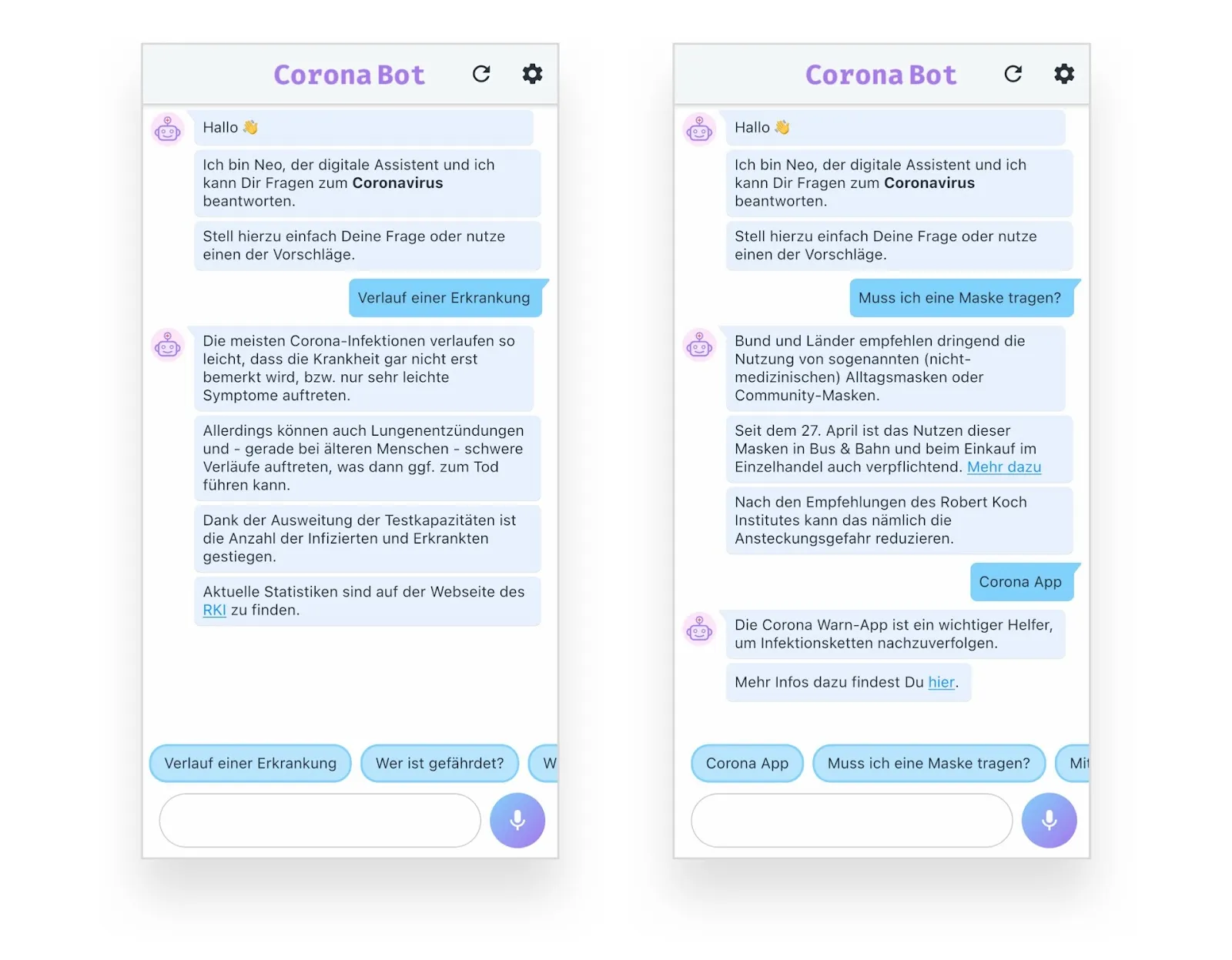
It would be particularly exciting here to offer those affected assistance in their respective native language to further reduce the hurdles in communication. This use case is therefore predestined for the Multi2ConvAI research project.
Voice assistant for quality assurance: Hands-free in quality control
In addition to chatbots, digital assistants are also finding use cases in companies: For example, voice assistants are predestined for use in quality control and maintenance processes because they offer three relevant advantages: First, the interaction is “hands-free” so that gloves can also be kept on, work can be performed with the hands as well as documented at the same time, and occupational safety can be additionally increased as a result. Second, data quality can be increased by the assistant directly validating the entries and, for example, pointing out deviations in tolerance ranges. And thirdly, voice assistants reduce onboarding and training times through their ease of use, as they can be operated intuitively and also allow questions to be asked in process steps.
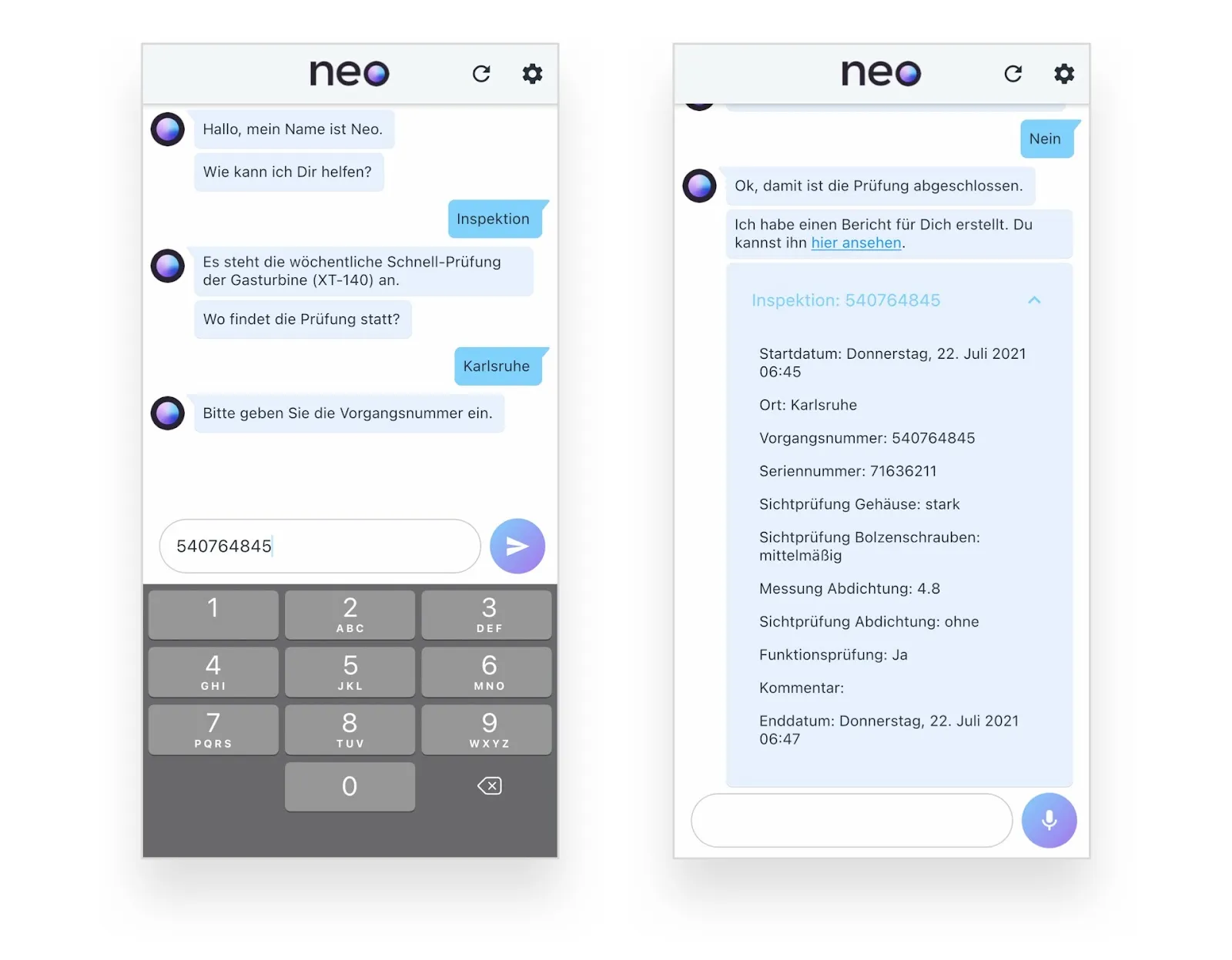
These use cases are very domain-specific and also use specialized vocabulary. From an NLP perspective, this is an exciting challenge with high practical relevance in the context of domain and language transferability.
Last-mile delivery: eyes on the road, hands on the wheel, and information in your ears
“Hands-free” interaction is also relevant in cars. Particularly in parcel delivery, crucial information must be searched for on available devices under time pressure, for instance, to navigate to the next stop or to retrieve information about the delivery process. A voice assistant for optimization on the “last mile” has similar effects as in quality management: Easy usability for faster onboarding, “hands-free” (and “eyes-free”) for more security, and the possibility to ask questions about specifics.
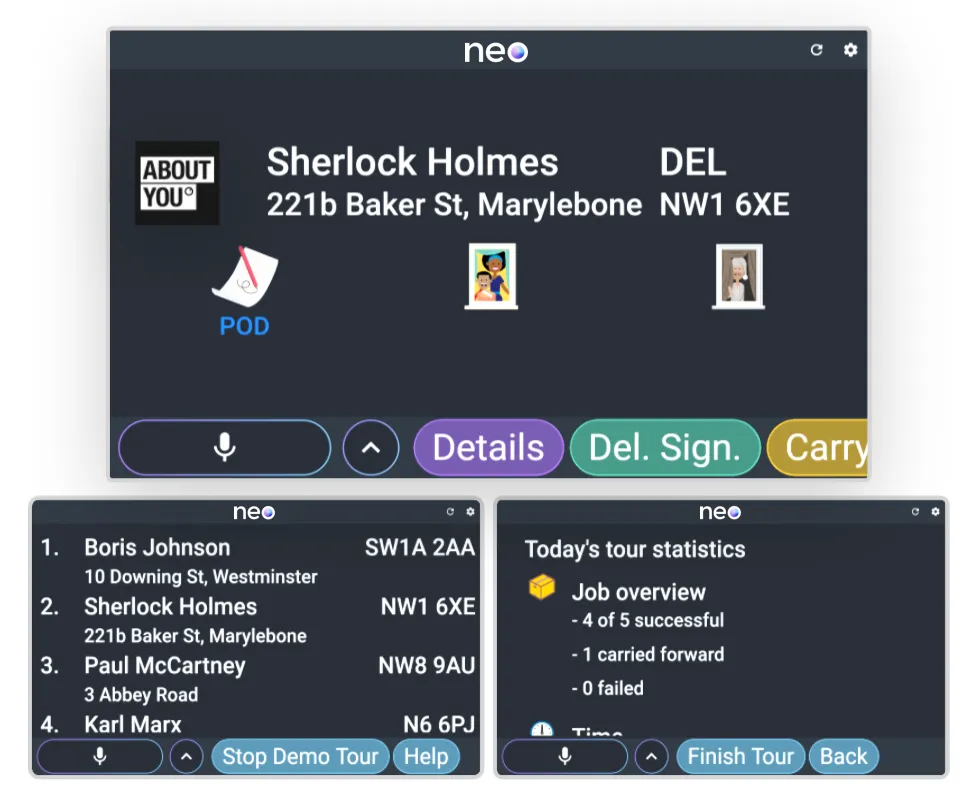
The topic of multilinguality is particularly relevant in the CEP industry (courier, express, and parcel service), since it often works across national borders and has a diverse workforce. From the point of view of training and dialog data, you also have an interesting topic field here with complex constellations of proper names, street and place names, and short commands with partly domain-specific vocabulary.
Outlook
Transferring models and dialogs to other domains and languages is still difficult in practice and involves enormous effort. Specialized vocabulary and editorial maintenance in particular often represent significant efforts that make translation or localization unprofitable. The Multi2ConvAI research project hopes to contribute to making digital assistants and chatbots more easily available and usable across domains and languages.